Back
BackProblem 8
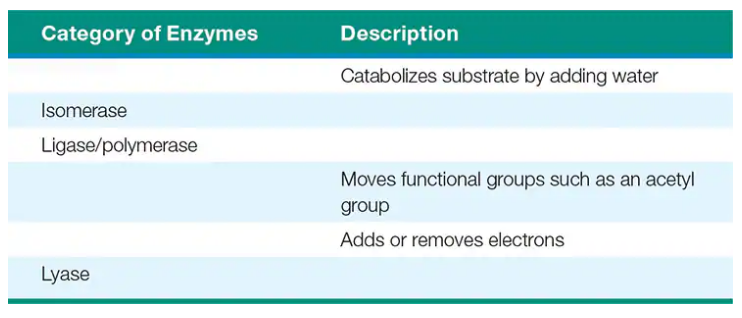
Complete the following chart:
The main coenzymes that carry electrons in catabolic pathways are _______ and ________.
Problem 9
The use of a proton motive force to generate ATP is __________.
Problem 1
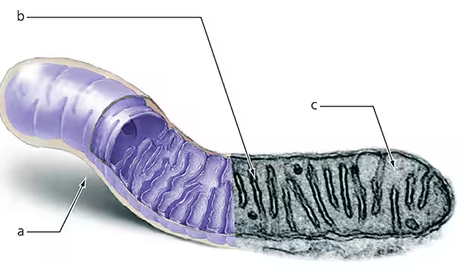
Label the mitochondrion to indicate the location of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and electron transport chains.
Problem 2
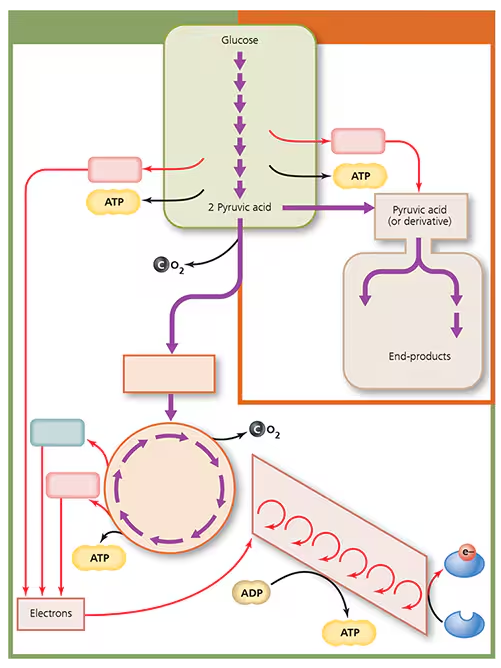
Label the diagram below to indicate acetyl-CoA, electron transport chain, FADH2, fermentation, glycolysis, citric acid cycle, NADH, and respiration. Indicate the net number of molecules of ATP that could be synthesized at each stage during bacterial respiration of one molecule of glucose.
Problem 3
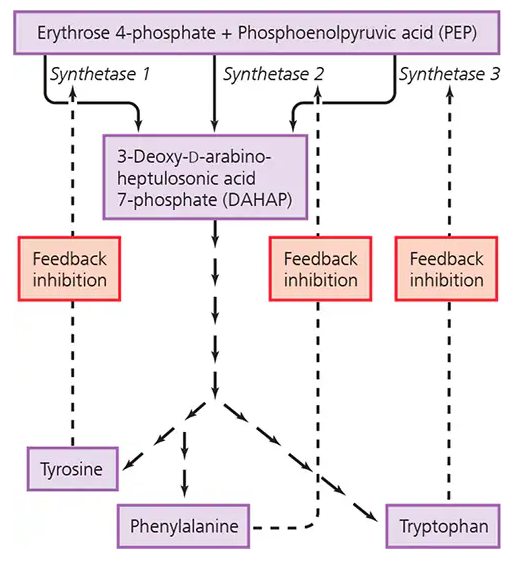
Examine the biosynthetic pathway for the production of the amino acids tryptophan, tyrosine, and phenylalanine in the figure. Where do the initial reactants (erythrose 4-phosphate and PEP) originate?
Problem 6
Facultative anaerobes can live under either aerobic or anaerobic conditions. What metabolic pathways allow these organisms to continue to harvest energy from sugar molecules in the absence of oxygen?
Problem 1
How does amination differ from transamination?
Problem 2
Why are enzymes necessary for anabolic reactions to occur in living organisms?
Problem 3
How do organisms control the rate of metabolic activities in their cells?
Problem 4
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor at a single allosteric site affect a whole pathway of enzymatic reactions?
Problem 5
Explain the mechanism of negative feedback with respect to enzyme action.
Problem 7
How does oxidation of a molecule occur without oxygen?
Problem 8
List at least four groups of microorganisms that are photosynthetic.
Problem 9
Why do we breathe oxygen and give off carbon dioxide?
Problem 10
Why do cyanobacteria and algae take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen?
Problem 11
What happens to the carbon atoms in sugar catabolized by Escherichia coli?
Problem 12
How do yeast cells make alcohol and cause bread to rise?
Problem 13
Where specifically does the most significant production of ATP occur in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Problem 14
Why are vitamins essential metabolic factors for microbial metabolism?
Problem 15
A laboratory scientist notices that a certain bacterium does not utilize lactose when glucose is available in its environment. Describe a cellular regulatory mechanism that would explain this observation.