Back
BackProblem 1
Classify the following vaccines by type. Which could cause the disease it is supposed to prevent?
a. Attenuated measles virus
b. Dead Rickettsia prowazekii
c. Vibrio cholerae toxoid
d. Hepatitis B antigen produced in yeast cells
e. Purified polysaccharides from Streptococcus pyogenes
f. H. influenzae polysaccharide bound to diphtheria toxoid
g. A plasmid containing genes for influenza A protein
Problem 2
Define the following terms, and give an example of how each reaction is used diagnostically:
a. Viral hemagglutination
b. Hemagglutination inhibition
c. Passive agglutination
Problem 3
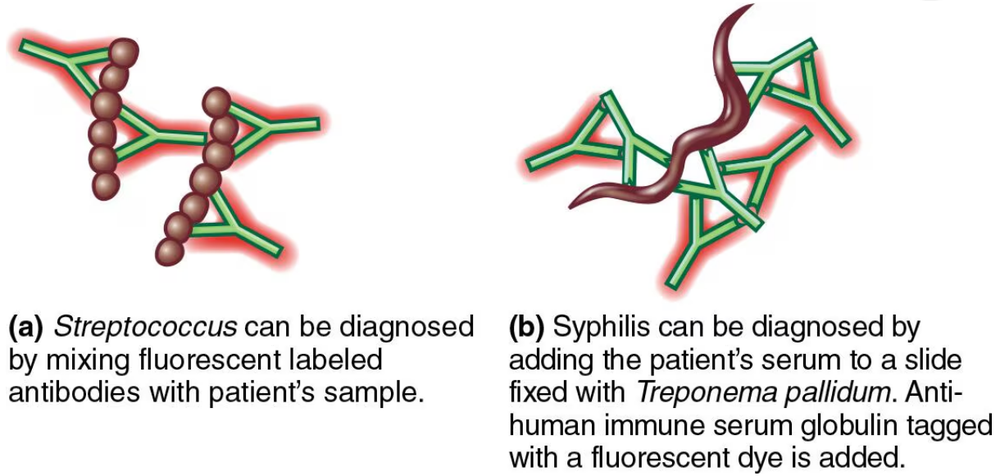
Label the components of the direct and indirect FA tests in the following situations. Which test is direct? Which test provides definitive proof of disease?
Problem 4
How are monoclonal antibodies produced?
Problem 5
Explain the effects of excess antigen and antibody on the precipitation reaction. How is the precipitin ring test different from an immunodiffusion test?
Problem 6
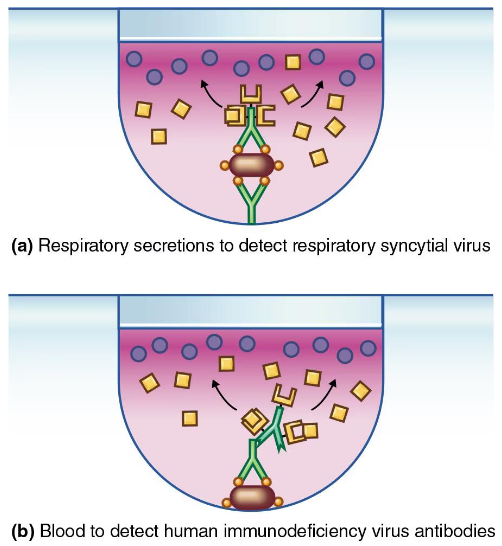
Label components of the direct and indirect ELISA tests in the following situations. Which test is direct? Which test provides definitive proof of disease?
Problem 8
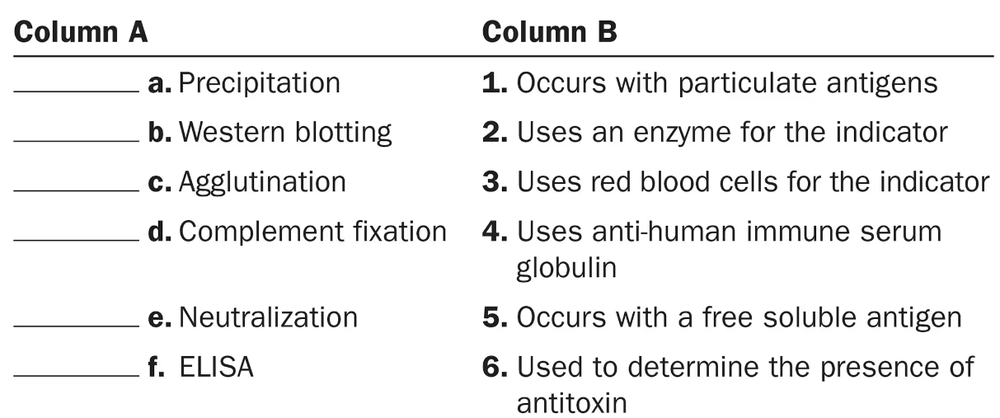
Match the following serological tests in column A to the descriptions in column B.
Problem 9
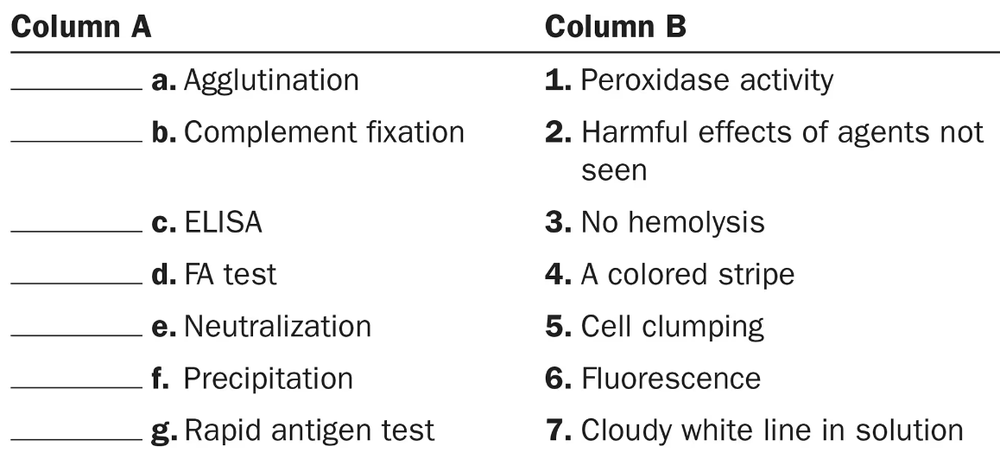
Match each of the following tests in column A to its positive reaction in column B.
Problem 10
A purified protein from Mycobacterium tuberculosis is injected into a person’s skin. A hardened, red area develops around the injection site within 3 days.
Problem 1
Use the following choices to answer questions 1 and 2:
a. Hemolysis
b. Hemagglutination
c. Hemagglutination inhibition
d. No hemolysis
e. Precipitin ring forms
Patient’s serum, influenza virus, sheep red blood cells, and anti-sheep red blood cells are mixed in a tube. What happens if the patient has antibodies against influenza?
Problem 2
Use the following choices to answer questions 1 and 2:
a. Hemolysis
b. Hemagglutination
c. Hemagglutination inhibition
d. No hemolysis
e. Precipitin ring forms
Patient’s serum, Chlamydia, guinea pig complement, sheep red blood cells, and anti-sheep red blood cells are mixed in a tube. What happens if the patient has antibodies against Chlamydia?
Problem 3
The examples in questions 1 and 2 are:
a. Direct tests
b. Indirect tests
Problem 4
Use the following choices to answer questions 4 and 5:
a. Anti-Brucella
b. Brucella
c. Substrate for the enzyme
Which is the third step in a direct ELISA test?
Problem 5
Use the following choices to answer questions 4 and 5:
a. Anti-Brucella
b. Brucella
c. Substrate for the enzyme
Which item is from the patient in an indirect ELISA test?
Problem 6
In an immunodiffusion test, a strip of filter paper containing diphtheria antitoxin is placed on a solid culture medium. Then bacteria are streaked perpendicular to the filter paper. If the bacteria are toxigenic,
a. The filter paper will turn red
b. A line of antigen–antibody precipitate will form
c. The cells will lyse
d. The cells will fluoresce
e. None of the above
Problem 7
Use the following choices to answer questions 7–9.
a. Direct fluorescent antibody
b. Indirect fluorescent antibody
c. Rabies immune globulin
d. Killed rabies virus
e. None of the above
Treatment given to a person bitten by a rabid bat.
Problem 8
Test used to identify rabies virus in the brain of a dog.
a. Direct fluorescent antibody
b. Indirect fluorescent antibody
c. Rabies immune globulin
d. Killed rabies virus
e. None of the above
Problem 9
Test used to detect the presence of antibodies in a patient’s serum.
a. Direct fluorescent antibody
b. Indirect fluorescent antibody
c. Rabies immune globulin
d. Killed rabies virus
e. None of the above
Problem 10
In an agglutination test, eight serial dilutions to determine antibody titer were set up: Tube 1 contained a 1:2 dilution; tube 2, a 1:4, and so on. If tube 5 is the last tube showing agglutination, what is the antibody titer?
a. 5
b. 1:5
c. 32
d. 1:32