Textbook Question
An object in simple harmonic motion has position function s(t), in inches, from an equilibrium point, as follows, where t is time in seconds.
𝒮(t) = 5 cos 2t
What is the amplitude of this motion?
607
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
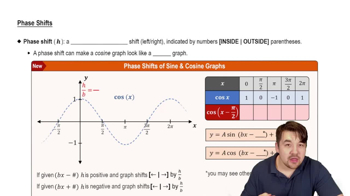


An object in simple harmonic motion has position function s(t), in inches, from an equilibrium point, as follows, where t is time in seconds.
𝒮(t) = 5 cos 2t
What is the amplitude of this motion?
For each function, give the amplitude, period, vertical translation, and phase shift, as applicable.
y = 3 - ¼ cos ⅔ x
Graph each function over a one-period interval.
y = 3 sec [(1/4)x]