Fill in the blanks in the following graph, which illustrates the decay curve of a radioactive element used to date fossil structures.

Describe three ways that evolution can occur via genetic drift.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Genetic Drift

Bottleneck Effect
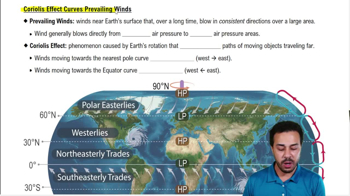
Founder Effect

The process of biological evolution
a. Is not supported by scientific evidence
b. Results in a change in the features of individuals in a population
c. Takes place over the course of generations
d. B and C are correct
e. A, B, and C are correct
In science, a theory is a(n)
a. Educated guess
b. Inference based on a lack of scientific evidence
c. Idea with little experimental support
d. Body of scientifically acceptable general principles
e. Statement of fact
Add labels to the figure that follows, which illustrates how Mycobacterium tuberculosis evolves when it is exposed to an antibiotic.
The theory of common descent states that all modern organisms
a. Can change in response to environmental change
b. Descended from a single common ancestor
c. Descended from one of many ancestors that originally arose on Earth
d. Have not evolved
e. Can be arranged in a hierarchy from 'least evolved' to 'most evolved'
