Use the following facts. If x represents an integer, then x+1 represents the next consecutive integer. If x represents an even integer, then x+2 represents the next consecutive even integer. If x represents an odd integer, then x+2 represents the next consecutive odd integer. Find two consecutive even integers whose product is 168.
Table of contents
- 0. Review of Algebra4h 18m
- 1. Equations & Inequalities3h 18m
- 2. Graphs of Equations1h 43m
- 3. Functions2h 17m
- 4. Polynomial Functions1h 44m
- 5. Rational Functions1h 23m
- 6. Exponential & Logarithmic Functions2h 28m
- 7. Systems of Equations & Matrices4h 5m
- 8. Conic Sections2h 23m
- 9. Sequences, Series, & Induction1h 22m
- 10. Combinatorics & Probability1h 45m
1. Equations & Inequalities
The Square Root Property
Problem 60
Textbook Question
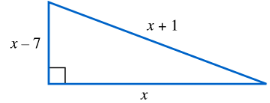
Dimensions of a Right Triangle The shortest side of a right triangle is 7 in. shorter than the middle side, while the longest side (the hypotenuse) is 1 in. longer than the middle side. Find the lengths of the sides.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Assign a variable to represent the length of the middle side. Let the middle side be \(x\) inches.
Express the shortest side in terms of \(x\). Since it is 7 inches shorter than the middle side, the shortest side is \(x - 7\) inches.
Express the longest side (hypotenuse) in terms of \(x\). Since it is 1 inch longer than the middle side, the hypotenuse is \(x + 1\) inches.
Use the Pythagorean theorem for right triangles, which states that the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides equals the square of the hypotenuse: \\$ (x - 7)^2 + x^2 = (x + 1)^2 $
Expand and simplify the equation, then solve the resulting quadratic equation for \(x\). After finding \(x\), substitute back to find the lengths of the shortest and longest sides.
 Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Verified video answer for a similar problem:This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above
Video duration:
5mPlay a video:
0 Comments
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (longest side) equals the sum of the squares of the other two sides. This relationship, a² + b² = c², is essential for finding unknown side lengths when two sides are known or expressed in terms of each other.
Algebraic Expressions and Variables
Using variables to represent unknown side lengths allows setting up equations based on given relationships. For example, if the middle side is x, the shortest side can be expressed as x - 7, and the hypotenuse as x + 1. This translation from words to algebraic expressions is crucial for solving the problem.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Introduction to Algebraic Expressions
Solving Quadratic Equations
After substituting the expressions into the Pythagorean theorem, the resulting equation is quadratic. Solving quadratic equations involves rearranging terms, factoring or using the quadratic formula, and interpreting the solutions in the context of the problem to find valid side lengths.
Recommended video:
Solving Quadratic Equations by Factoring

 6:12m
6:12mWatch next
Master Solving Quadratic Equations by the Square Root Property with a bite sized video explanation from Patrick
Start learningRelated Videos
Related Practice
Textbook Question
635
views
