Ch.16 - Acids and Bases

Chapter 16, Problem 136
The AIDS drug zalcitabine (also known as ddC) is a weak base with a pKb of 9.8. What percentage of the base is protonated in an aqueous zalcitabine solution containing 565 mg/L?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
First, we need to understand that the percentage of the base that is protonated in a solution is determined by the pH of the solution. The pKb value tells us how easily the base accepts a proton (H+). A higher pKb value means the base is weaker, and less likely to accept a proton.
Next, we need to calculate the pH of the solution. We can use the formula pH = 14 - pKb. This formula is derived from the relationship between pKb and pKa (pKa + pKb = 14), and the relationship between pH and pKa (pH = pKa when the solution is at half equivalence point).
Once we have the pH of the solution, we can calculate the ratio of protonated to unprotonated base using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: pH = pKa + log([A-]/[HA]). In this case, [A-] is the concentration of the unprotonated base and [HA] is the concentration of the protonated base.
Rearrange the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to solve for [HA]/[A-], which gives us the ratio of protonated to unprotonated base: [HA]/[A-] = 10^(pKa - pH).
Finally, to find the percentage of the base that is protonated, divide the concentration of the protonated base by the total concentration of the base (which is the sum of the protonated and unprotonated concentrations), and multiply by 100.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
5mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
pKb and pKa Relationship
The pKb value is a measure of the basicity of a compound, with lower values indicating stronger bases. The relationship between pKb and pKa is given by the equation pKa + pKb = 14. This relationship is crucial for understanding the protonation state of a weak base in solution, as it allows us to calculate the pKa from the given pKb.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Ka and Kb Relationship
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation relates the pH of a solution to the pKa of an acid and the ratio of the concentrations of its protonated and deprotonated forms. For a weak base, the equation can be rearranged to find the percentage of the base that is protonated, which is essential for determining the behavior of zalcitabine in solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
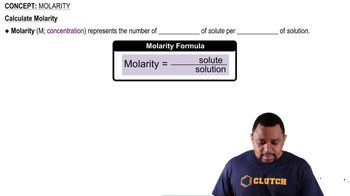
Concentration and Molarity
Concentration, often expressed in mg/L or molarity (mol/L), is a measure of the amount of solute in a given volume of solution. To determine the percentage of zalcitabine that is protonated, it is necessary to convert the given mass concentration (565 mg/L) into molarity, which involves knowing the molar mass of zalcitabine. This conversion is fundamental for applying the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Molarity Concept
Related Practice
