Textbook Question
How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
661
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


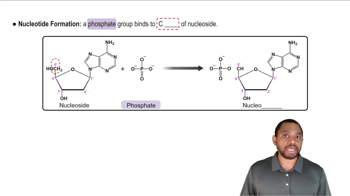
How are the two strands of nucleic acid in DNA held together?
Write the base sequence and label the 3' and 5' ends of the complementary strand for a segment of DNA with the following base sequences:
b. 5'CCCCTTTT3'
Write the base sequence and label the 3' and 5' ends of the complementary strand for a segment of DNA with the following base sequences:
d. 5'CGCGATATTA3'
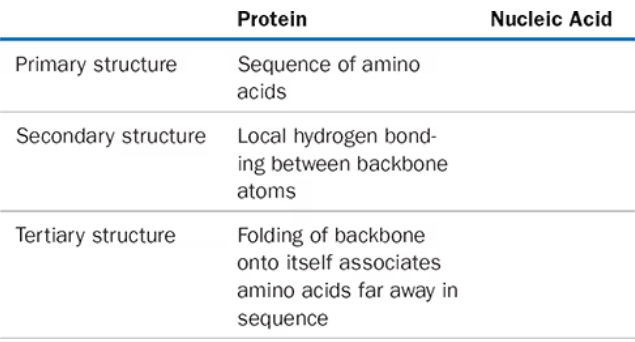
List the similarities and differences in the secondary structure of a protein and the secondary structure of DNA.
Name the three types of RNA and their functions.
List the mRNA bases that complement the bases A, T, G, and C in DNA.