Vitamins are a diverse group of compounds that must be present in the diet. List four functions of vitamins in the body.

Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
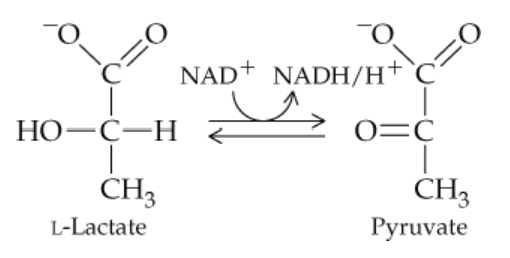
c. What is the substrate for the reaction as written?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Substrate
Reaction Mechanism

Enzyme Specificity

Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
a. The enzyme involved in this reaction belongs to what class of enzymes?
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
b. Since hydrogens are removed, the enzyme belongs to what subclass of the enzyme class from part (a)?
Answer questions (a)–(e) concerning the following reaction:
d. What is the product for the reaction as written?
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(a) increasing the substrate concentration at a constant inhibitor concentration
Explain how the following changes affect the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an uncompetitive inhibitor:
(b) decreasing the inhibitor concentration at a constant substrate concentration.
