Name the nucleoside shown here. Copy the structure, and number the C and N atoms (refer to Table 26.1).
Ch.26 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis

Chapter 26, Problem 8a
Write the complementary sequence of bases for each DNA strand shown next.
a. 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the base-pairing rules for DNA: Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G).
Write the complementary base for each nucleotide in the given sequence, starting from the 5′ end of the original strand. For example, if the original strand has 'T', the complementary base will be 'A'.
Ensure the complementary strand is written in the 3′ to 5′ direction, as DNA strands are antiparallel.
For the given sequence 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′, apply the base-pairing rules to each nucleotide: T pairs with A, A pairs with T, C pairs with G, and G pairs with C.
Write the final complementary sequence in the 3′ to 5′ direction, ensuring the correct orientation of the strand.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Structure
DNA is composed of two strands forming a double helix, with each strand made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The four types of nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). The bases pair specifically: A with T and C with G, which is crucial for understanding complementary sequences.
Recommended video:
Guided course
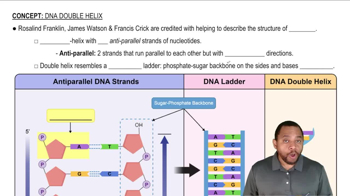
DNA Double Helix Concept 1
Complementary Base Pairing
Complementary base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA. Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T), and cytosine pairs with guanine (C-G). This pairing is essential for DNA replication and transcription, as it ensures that the genetic information is accurately copied and transmitted. Understanding this concept is key to determining the complementary sequence of a given DNA strand.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Base Pairing Concept 1
5' and 3' Ends of DNA Strands
DNA strands have directionality, indicated by the 5' (five-prime) and 3' (three-prime) ends. The 5' end has a phosphate group, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group. When writing or reading DNA sequences, it is important to maintain this orientation, as it affects how the strands interact during processes like replication and transcription. This directional aspect is crucial for accurately determining complementary sequences.
Recommended video:
Guided course
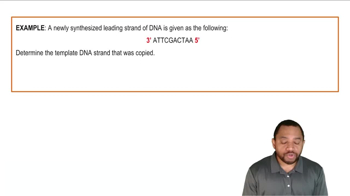
Intro to DNA Replication Example 3
Related Practice
Textbook Question
525
views
Textbook Question
Write the full name of:
a. dUMP
1213
views
Textbook Question
Name the bases in the pentanucleotide with the sequence G-A-U-C-A. Does this come from RNA or DNA? Explain.
888
views
Textbook Question
Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
851
views
Textbook Question
Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.
1040
views
Textbook Question
DNA and RNA, like proteins, can be denatured to produce unfolded or uncoiled strands. Heating DNA to what is referred to as its “melting temperature” denatures it (the two strands of the double helix become separated). Why does a longer strand of DNA have a higher melting temperature than a shorter one?
690
views
