Name the bases in the pentanucleotide with the sequence G-A-U-C-A. Does this come from RNA or DNA? Explain.
Ch.26 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis

Chapter 26, Problem 10
Is a DNA molecule neutral, negatively charged, or positively charged? Explain.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
DNA molecules are composed of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base.
The phosphate group in each nucleotide contains a negatively charged oxygen atom, which gives the DNA molecule an overall negative charge.
These negatively charged phosphate groups are present along the backbone of the DNA molecule, making the entire structure negatively charged.
The negative charge of DNA is important for its interactions with other molecules, such as positively charged proteins (e.g., histones) that help in DNA packaging.
In summary, a DNA molecule is negatively charged due to the presence of phosphate groups in its structure.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
DNA Structure
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule composed of two strands that coil around each other to form a double helix. Each strand is made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. The phosphate groups in the backbone of the DNA contribute to its overall charge.
Recommended video:
Guided course
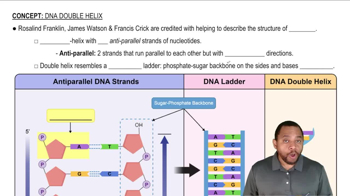
DNA Double Helix Concept 1
Charge of DNA
DNA molecules are negatively charged due to the presence of phosphate groups in their structure. Each phosphate group carries a negative charge, which results in the overall negative charge of the DNA molecule. This charge plays a crucial role in the interactions of DNA with proteins and other molecules in the cell.
Recommended video:
Guided course
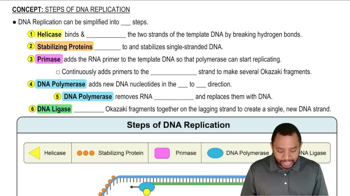
Steps of DNA Replication Concept 1
Biological Implications of Charge
The negative charge of DNA is significant for its biological functions, including its interaction with positively charged proteins, such as histones, which help package DNA into chromatin. This charge also influences the behavior of DNA during processes like electrophoresis, where DNA fragments are separated based on size and charge.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Periodic Table: Transition Metals Charges Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
888
views
Textbook Question
Write the complementary sequence of bases for each DNA strand shown next.
a. 5′T-A-T-A-C-T-G 3′
661
views
Textbook Question
Draw the structures of adenine and uracil (which replaces thymine in RNA), and show the hydrogen bonding that occurs between them.
851
views
Textbook Question
DNA and RNA, like proteins, can be denatured to produce unfolded or uncoiled strands. Heating DNA to what is referred to as its “melting temperature” denatures it (the two strands of the double helix become separated). Why does a longer strand of DNA have a higher melting temperature than a shorter one?
690
views
Textbook Question
What are Okazaki fragments? What role do they serve in DNA metabolism?
589
views
Textbook Question
What is the difference between DNA polymerase and DNA ligase?
833
views
