A 1.00 mL sample of red blood cells containing chromium-51 as a tracer was injected into a patient. After several hours, a 5.00 mL sample of blood was drawn and its activity compared to the activity of the injected tracer sample. If the collected sample activity was 0.10% of the original tracer, calculate the total blood volume of the patient (see the Chemistry in Action 'Medical Uses of Radioactivity,' p. 338).
Ch.11 Nuclear Chemistry

Chapter 11, Problem 7
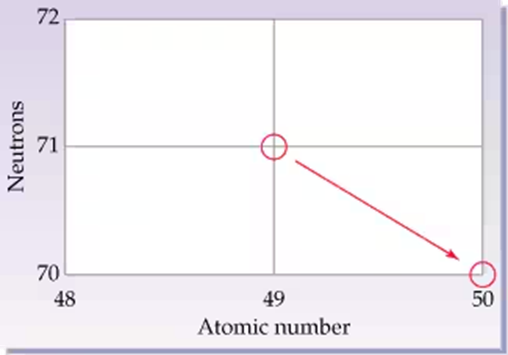
The red arrow in the graph (see margin) indicates the changes that occur in the nucleus of an atom during a nuclear reaction. Identify the isotopes involved as product and reactant, and name the type of decay process.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Analyze the graph. The red arrow indicates a change in the atomic number from 28 to 29 and a decrease in the number of neutrons from 36 to 35. This suggests a nuclear reaction where the nucleus of the atom undergoes a transformation.
Step 2: Identify the reactant isotope. The initial point on the graph corresponds to an atomic number of 28 and 36 neutrons. The atomic number represents the element nickel (Ni), and the mass number is calculated as the sum of protons and neutrons: 28 + 36 = 64. Thus, the reactant isotope is Ni-64.
Step 3: Identify the product isotope. The final point on the graph corresponds to an atomic number of 29 and 35 neutrons. The atomic number represents the element copper (Cu), and the mass number is calculated as the sum of protons and neutrons: 29 + 35 = 64. Thus, the product isotope is Cu-64.
Step 4: Determine the type of decay process. The increase in atomic number by 1 and the decrease in neutrons by 1 indicate that a neutron has been converted into a proton. This is characteristic of beta decay, specifically beta-minus decay, where a neutron emits an electron (beta particle) and transforms into a proton.
Step 5: Summarize the reaction. The nuclear reaction involves the beta-minus decay of Ni-64, resulting in the formation of Cu-64. This process is represented as: .

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isotopes
Isotopes are variants of a particular chemical element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron count results in varying atomic masses. In nuclear reactions, isotopes can be transformed into one another, which is crucial for understanding the reactants and products involved in decay processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Isotopes
Nuclear Decay
Nuclear decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by emitting radiation. This can occur in various forms, including alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay. The type of decay affects the identity of the isotopes involved, as it determines how the nucleus changes during the reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alpha Decay Concept 1
Beta Decay
Beta decay is a specific type of nuclear decay where a neutron in the nucleus is transformed into a proton, emitting a beta particle (an electron or positron) in the process. This results in an increase in the atomic number of the element by one, while the mass number remains unchanged. The graph indicates a transition from one isotope to another, highlighting the beta decay process.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Beta Decay Example 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1415
views
Textbook Question
A β-emitting radiation source gives 250 units of radiation at a distance of 4.0 m. At what distance does the radiation drop to one-tenth its original value?
1485
views
1
rank
Textbook Question
A solution of selenium-75, a radioisotope used in the diagnosis of pancreatic disease, is found just prior to administration to have an activity of 44 μCi/mL. If 3.98 mL were delivered intravenously to the patient, what dose of Se-75 (in μCi) did the patient receive?
2120
views
