Textbook Question
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
b. hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms
646
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
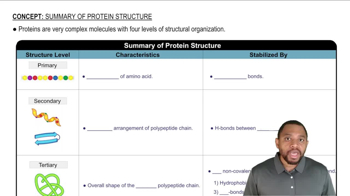
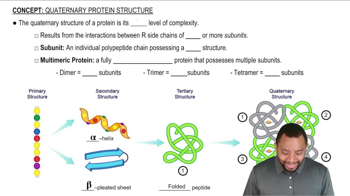

Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
b. hydrogen bonding between backbone atoms
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
d. intermolecular forces between R groups
Identify the level of protein structure associated with each of the following:
b. disulfide bridge
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
a. collagen
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
c. hemoglobin
For each of the following proteins, note whether the main secondary structure feature is α helix, β-pleated sheet, or both.
e. hexokinase