Textbook Question
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
b. citric acid cycle
1343
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
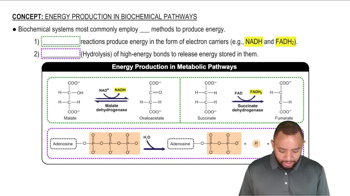

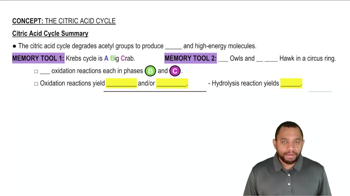
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
b. citric acid cycle
Name the location in the cell where the following catabolic processes take place:
c. β oxidation
Identify each pathway as anabolic or catabolic.
a. gluconeogenesis
Identify the type of food—carbohydrate, fat, or protein—that gives each of the following digestion products:
b. fatty acid
Identify the type of food—carbohydrate, fat, or protein—that gives each of the following digestion products:
d. glycerol
How and where does sucrose undergo digestion in the body? Name the products.