Textbook Question
What is the effect of proton accumulation in the intermembrane space?
1495
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
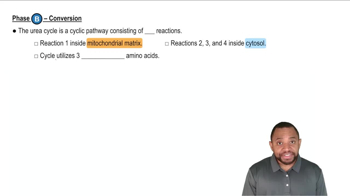

What is the effect of proton accumulation in the intermembrane space?
How many ATP are produced when glucose is oxidized to pyruvate compared to when glucose is oxidized to CO2 and H2O?
Name the reaction that removes nitrogen from an α-amino acid, forming an α-keto acid.
What metabolic substrate(s) can be produced from the carbon atoms of each of the following amino acids?
c. methionine
Consider the complete oxidation of capric acid, a saturated fatty acid, [10:0].
c How many ATP are generated from the complete oxidation of capric acid?
Consider the complete oxidation of arachidic acid, a saturated fatty acid, [20:0].
b. How many cycles of β oxidation occur?