Textbook Question
Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) Wine (containing ethanol, CH3CH2OH) sours to vinegar (CH3COOH).
766
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) Wine (containing ethanol, CH3CH2OH) sours to vinegar (CH3COOH).
Are the substances shown in italics undergoing oxidation or reduction?
(c) The biomolecule FADH2 loses hydrogen, becoming FAD.
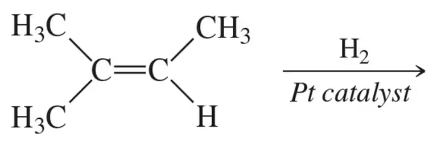
Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(c)
Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(c)
Identify the main organic reaction shown as condensation, hydrolysis, oxidation, or reduction:
(b)