Textbook Question
Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(a)
711
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(a)
Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(c)
Write the products for the following hydrogenation reactions:
(c)
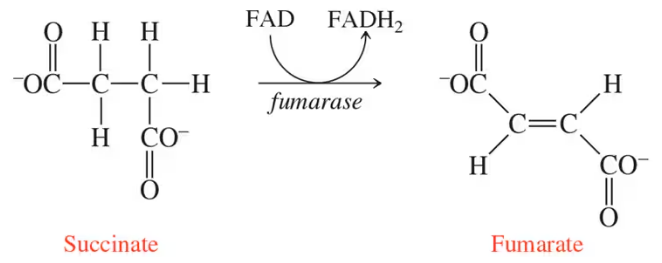
Determine whether each of the following organic reactions is an oxidation or a reduction reaction. (Only the organic compounds are shown.)
(b)
Write the products of the following reactions:
(b)
Write the products of the following reactions:
(a)