Pure acetic acid, which gives the sour taste to vinegar, has a melting point of 16.7 °C and a boiling point of 118 °C . Predict the physical state of acetic acid when the ambient temperature is 10 °C .
Ch.1 Matter and Measurements

Chapter 1, Problem 32
Assume that you are delivering a solution sample from a pipette. Figures (a) and (b) show the volume level before and after dispensing the sample, respectively. State the liquid level (in mL) before and after dispensing the sample, and calculate the volume of the sample.
<IMAGE>
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Observe the liquid level in figure (a), labeled 'START'. The liquid level is at 0.3 mL.
Step 2: Observe the liquid level in figure (b), labeled 'STOP'. The liquid level is at 0.2 mL.
Step 3: To calculate the volume of the sample dispensed, subtract the liquid level after dispensing (STOP) from the liquid level before dispensing (START). Use the formula: Volume dispensed = START volume - STOP volume.
Step 4: Substitute the observed values into the formula: Volume dispensed = 0.3 mL - 0.2 mL.
Step 5: Perform the subtraction to determine the volume of the sample dispensed. The result will be the volume in mL.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Graduated Cylinder Measurement
Graduated cylinders are used to measure the volume of liquids accurately. The scale on the cylinder indicates the volume at various levels, typically in milliliters (mL). Understanding how to read these measurements is crucial for determining the liquid levels before and after dispensing a sample.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Measuring Radioactivity Concept 1
Volume Calculation
Volume calculation involves determining the difference in liquid levels before and after dispensing a sample. This is done by subtracting the final volume from the initial volume, providing the volume of the liquid dispensed. Accurate calculations are essential for precise scientific measurements.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Calculate Oxidation Numbers
Pipetting Technique
Pipetting is a technique used to transfer a specific volume of liquid from one container to another. Proper pipetting technique ensures that the correct volume is dispensed, which is critical in experiments and laboratory settings. Understanding how to use a pipette effectively is fundamental for accurate liquid handling.
Recommended video:
Guided course
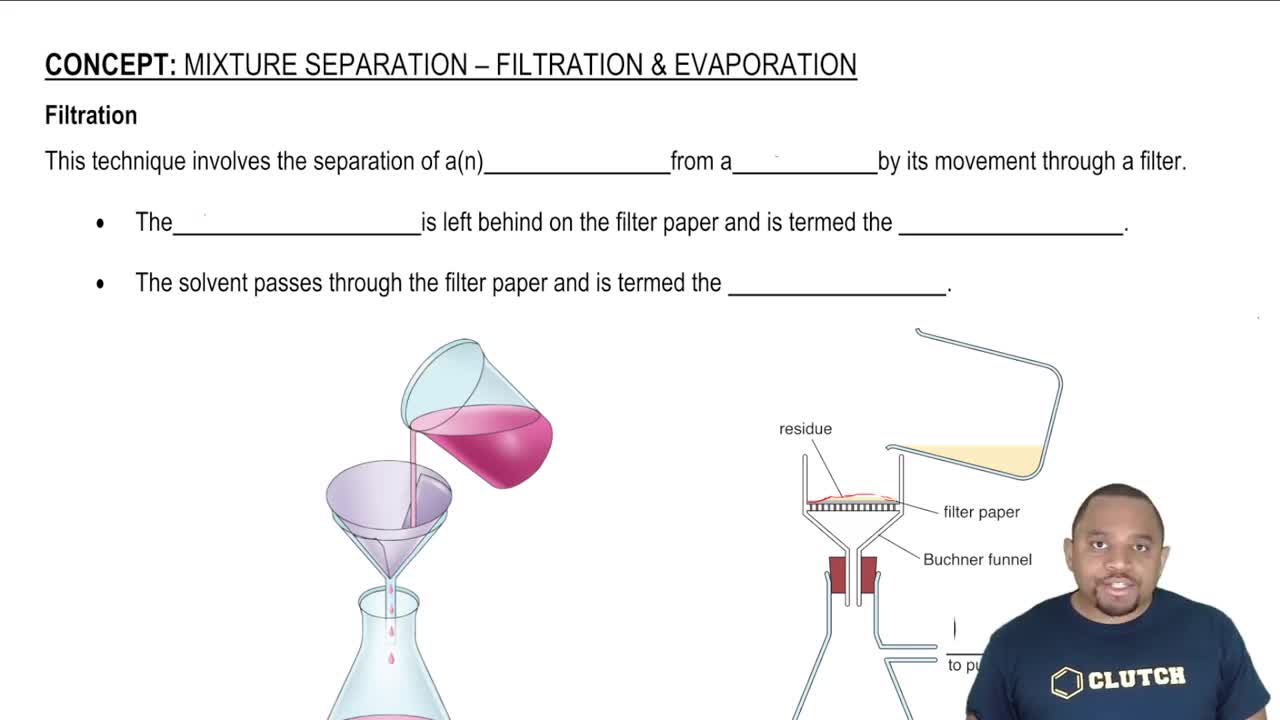
Filtration and Evaporation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2095
views
Textbook Question
Assuming that Coca-Cola has the same specific heat as water, how much energy in calories is removed when 350 g of Coca-Cola (about the contents of one 12 oz can) is cooled from room temperature (25 °C) to refrigerator temperature (3 °C)?
1698
views
Textbook Question
What is the specific gravity of the following solution?
<IMAGE>
2217
views
Textbook Question
Assume that identical hydrometers are placed in ethanol (sp gr 0.7893) and in chloroform (sp gr 1.4832). In which liquid will the hydrometer float higher? Explain.
940
views
Textbook Question
What is the difference between a physical change and a chemical change?
2339
views
Textbook Question
Name and describe the three states of matter.
2548
views
