Textbook Question
Electrostatic potential maps of acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) are shown. Identify the most acidic hydrogen in each, and tell which of the two is likely to be the stronger acid.
<IMAGE>
1872
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

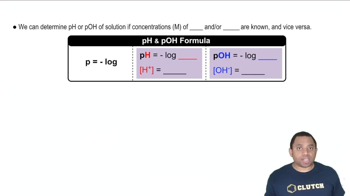

Electrostatic potential maps of acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) are shown. Identify the most acidic hydrogen in each, and tell which of the two is likely to be the stronger acid.
<IMAGE>
What happens when a strong acid such as HBr is dissolved in water?
What happens when a weak acid such as CH3CO2H is dissolved in water?
What happens when a weak base such as NH3 is dissolved in water?
What is the difference between a monoprotic acid and a diprotic acid? Give an example of each.
What is the difference between H+ and H3O+?