Textbook Question
From this electrostatic potential map of the amino acid alanine, identify the most acidic hydrogens in the molecule:
<IMAGE>
1476
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


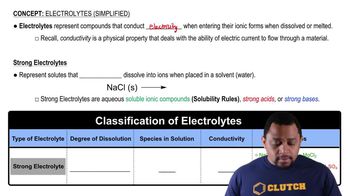
From this electrostatic potential map of the amino acid alanine, identify the most acidic hydrogens in the molecule:
<IMAGE>
Show how ethylamine (C2H5NH2) reacts with hydrochloric acid to form an ethylammonium salt.
Electrostatic potential maps of acetic acid (CH3CO2H) and ethyl alcohol (CH3CH2OH) are shown. Identify the most acidic hydrogen in each, and tell which of the two is likely to be the stronger acid.
<IMAGE>
What happens when a weak acid such as CH3CO2H is dissolved in water?
What happens when a strong base such as KOH is dissolved in water?
What happens when a weak base such as NH3 is dissolved in water?