Potassium, a silvery metal, reacts with bromine, a corrosive, reddish liquid, to yield potassium bromide, a white solid. Write the balanced equation, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
Ch.5 Classification & Balancing of Chemical Reactions

Chapter 5, Problem 20
An aqueous solution of a cation (represented as blue spheres in the diagram) is allowed to mix with a solution of an anion (represented as green spheres) and the following result is obtained:
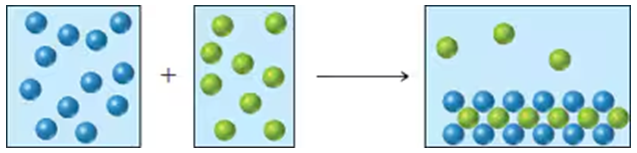
Which combinations of cation and anion, chosen from the following lists, are compatible with the observed results? Explain.
Cations: Na+, Ca2+, Ag+, Ni2+
Anions: Cl−, CO23–, CrO42–, NO3–
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Analyze the image provided. The diagram shows two solutions being mixed: one containing green spheres (representing anions) and the other containing red spheres (representing cations). After mixing, a solid precipitate forms at the bottom of the container, indicating that a chemical reaction has occurred and a precipitate has formed.
Step 2: Understand the concept of solubility rules. Precipitation occurs when the product of a reaction between a cation and an anion is insoluble in water. Use solubility rules to determine which combinations of cations and anions can form an insoluble compound.
Step 3: Evaluate the possible combinations of cations and anions provided in the problem. The cations are Na+, Ca2+, Ag+, and Ni2+, and the anions are Cl−, CO3^2−, CrO4^2−, and NO3−. Cross-reference these ions with solubility rules to identify which combinations produce an insoluble compound.
Step 4: Apply solubility rules to each combination. For example, Ag+ often forms insoluble compounds with Cl− (AgCl is insoluble), while Na+ typically forms soluble compounds with all the anions listed. Similarly, Ca2+ can form insoluble compounds with CO3^2− (CaCO3 is insoluble). Continue this process for all combinations.
Step 5: Based on the solubility rules and the observed precipitation in the diagram, identify the specific cation and anion pair that is compatible with the results. Ensure the pair corresponds to an insoluble compound forming a precipitate, as shown in the image.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
3mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when cations (positively charged ions) and anions (negatively charged ions) combine due to electrostatic forces. The stability of these compounds depends on the charge and size of the ions involved. In the context of the question, understanding how different cations and anions interact is crucial for predicting which combinations will form stable ionic compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Naming Ionic Compounds
Solubility Rules
Solubility rules are guidelines that help predict whether an ionic compound will dissolve in water. Certain combinations of cations and anions are known to be soluble or insoluble based on these rules. For example, compounds containing Na+ or NO3− are generally soluble, while others may form precipitates. This concept is essential for determining the compatibility of the given cations and anions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Solubility Rules
Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions occur when two solutions containing soluble salts are mixed, resulting in the formation of an insoluble compound that precipitates out of solution. The image illustrates this process, showing layered spheres that suggest a solid formation. Identifying which combinations of cations and anions lead to precipitation is key to answering the question effectively.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Alcohol Reactions: Dehydration Reactions Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1881
views
Textbook Question
Assume that the mixture of substances in drawing (a) undergoes a reaction. Which of the drawings (b)–(d) represent a product mixture consistent with the law of conservation of mass?
1902
views
Textbook Question
Reaction of A (green spheres) with B (blue spheres) is shown in the following diagram:
Which equation best describes the reaction?
a. A2 + 2 B → A2B2
b. 10 A + 5 B2 → 5 A2B2
c. 2 A + B2 → A2B2
d. 5 A + 5 B2 → 5 A2B2
1267
views
Textbook Question
What is meant by the term 'balanced equation'?
2437
views
Textbook Question
Why is it not possible to balance an equation by changing the subscript on a substance, say from H2O to H2O2?
2219
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following equations are balanced? Balance those that need it.
a. CaC2 + 2 H2O → Ca(OH)2 +C2H2
b. C2H8N2 + 2 N2O4 → 2 N2 + 2 CO2 + 4 H2O
c. 3 MgO + 2 Fe → Fe2O3 + 3 Mg
d. N2O → N2 + O2
1934
views
