Identify the oxidized reactant, the reduced reactant, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent in the following reactions:
a. Fe(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + Cu(s)
b. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
c. 2 Al(s) + Cr2O3(s) → 2 Cr(s) + Al2O3(s)

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Identify the oxidized reactant, the reduced reactant, the oxidizing agent, and the reducing agent in the following reactions:
a. Fe(s) + Cu2+(aq) → Fe2+(aq) + Cu(s)
b. Mg(s) + Cl2(g) → MgCl2(s)
c. 2 Al(s) + Cr2O3(s) → 2 Cr(s) + Al2O3(s)
Potassium, a silvery metal, reacts with bromine, a corrosive, reddish liquid, to yield potassium bromide, a white solid. Write the balanced equation, and identify the oxidizing and reducing agents.
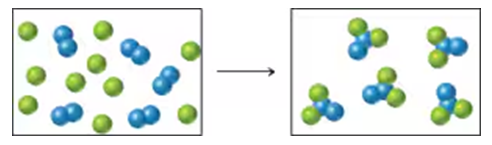
Assume that the mixture of substances in drawing (a) undergoes a reaction. Which of the drawings (b)–(d) represent a product mixture consistent with the law of conservation of mass?
An aqueous solution of a cation (represented as blue spheres in the diagram) is allowed to mix with a solution of an anion (represented as green spheres) and the following result is obtained:
Which combinations of cation and anion, chosen from the following lists, are compatible with the observed results? Explain.
Cations: Na+, Ca2+, Ag+, Ni2+
Anions: Cl−, CO23–, CrO42–, NO3–
What is meant by the term 'balanced equation'?
Why is it not possible to balance an equation by changing the subscript on a substance, say from H2O to H2O2?