Textbook Question
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
a.
779
views

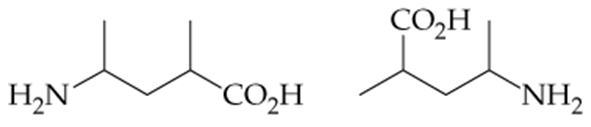
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
a.
Convert the following line structures to condensed structures:
b.
Draw both condensed and line structures for the chemicals listed in Problem 12.1.
a.
b.
c.
d.
What are the IUPAC names of the following alkanes?
a.
Draw both condensed and line structures corresponding to the following IUPAC names and label each carbon as primary, secondary, tertiary, or quaternary.
c. 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane
Draw and name alkanes that meet the following descriptions:
a. A 5-carbon alkane with a tertiary carbon atom