Textbook Question
Give an example of a compound that meets the following descriptions:
b. A cycloalkane with three substituents
886
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

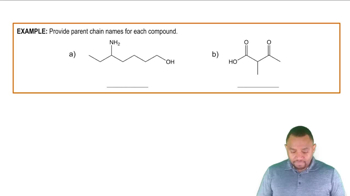

Give an example of a compound that meets the following descriptions:
b. A cycloalkane with three substituents
Write condensed structures for the following molecular formulas. More than one isomer will be required for each.
a. Isomers of C8H18 that contain two methyl groups and a longest chain of 4 carbons
How many straight-chain isomers can you write that fit the following descriptions? See Worked Example 12.12 for guidance.
b. Amines (―NH2) with a longest chain of 7 carbons
Which of the following pairs of structures are identical, which are isomers, and which are unrelated?
a.
What is wrong with the following structures?
a. CH3=CHCH2CH2OH
There are two things wrong with the following structure. What are they?