Textbook Question
Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
a. 4-tert-Butyl-2-methylheptane
1064
views

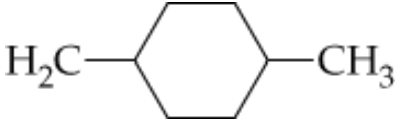
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance



Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
a. 4-tert-Butyl-2-methylheptane
Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
c. 4,4-Diethyl-3-methyloctane
Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
d. 3-Ethyl-1-isopropyl-5-methylcycloheptane
The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
a.
The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
b.
The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
c.