Textbook Question
What are the IUPAC names of the following alkanes?
f.
1633
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


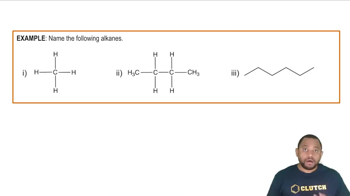
What are the IUPAC names of the following alkanes?
f.
Give IUPAC names for the five isomers with the formula C6H14.
Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
a. 4-tert-Butyl-2-methylheptane
Write condensed structures for the following compounds:
d. 3-Ethyl-1-isopropyl-5-methylcycloheptane
Name the following cycloalkanes:
c.
The following names are incorrect. Tell what is wrong with each, and provide the correct names.
a.