What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
c.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

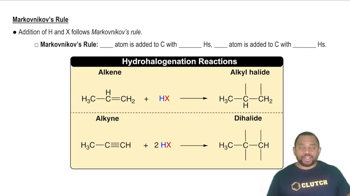
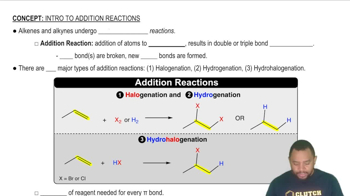
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
c.
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
d.
2,2,3,3-Tetrabromopentane can be prepared by an addition reaction of excess Br2 with an alkyne. Draw the structure of the alkyne and name it.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is often used in hair sprays to hold hair in place. Draw a few units of the PVP polymer. The vinylpyrrolidone monomer unit has the following structure:
For each of the following reagents, decide whether chlorobenzene will react with it or not, and, if it does, draw and name the products expected from the reaction.
c. HNO3 and H2SO4 catalyst
Aromatic compounds do not normally react with hydrogen in the presence of a palladium catalyst but will if very high pressures (200 atm) and high temperatures are used. Under these conditions, toluene adds three molecules of H2 to give an alkane addition product. What is a likely structure for the product?