What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
a.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

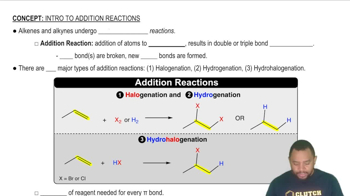
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
a.
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
c.
What alkene could you use to make the following products? Draw the structure of the alkene, and tell what other reagent is also required for the reaction to occur.
d.
1-Pentyne reacts with HBr in a 1:1 molar ratio to yield two different addition products, both being bromopentenes and having the chemical formula C5H9Br. Draw the structures of two possible products.
Polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is often used in hair sprays to hold hair in place. Draw a few units of the PVP polymer. The vinylpyrrolidone monomer unit has the following structure:
For each of the following reagents, decide whether chlorobenzene will react with it or not, and, if it does, draw and name the products expected from the reaction.
c. HNO3 and H2SO4 catalyst