Textbook Question
Ethers have some slight solubility in water. Explain this using the concept of hydrogen bonding.
39
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Ethers have some slight solubility in water. Explain this using the concept of hydrogen bonding.
Rank the following according to boiling point, highest to lowest:
a. CH3CH2CH2OH
b. CH3CH2(OH)CH2OH
c. CH3CH2CH3
d. CH2(OH)CH(OH)CH2OH
For each of the following molecules, (i) redraw using line structure format, (ii) identify its hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts, and (iii) predict its solubility in water.
c.
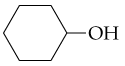
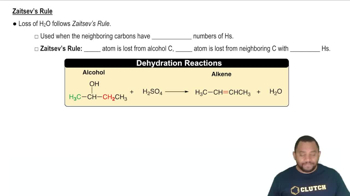
What alcohols yield the following alkenes as the major product on dehydration?
b.
What products would you expect from oxidation of the following alcohols?
a. CH3CH2CH2OH
b.
c.
From what alcohols might the following carbonyl-containing products have been made (red = O, reddish-brown = Br)?
(a) <IMAGE>
(b) <IMAGE>