Textbook Question
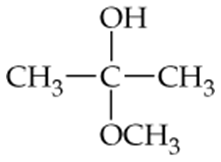
For each compound shown next (a–d), indicate whether the compound is polar or nonpolar, and whether it is soluble or insoluble in water.
a.
b.
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
d.
26
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

For each compound shown next (a–d), indicate whether the compound is polar or nonpolar, and whether it is soluble or insoluble in water.
a.
b.
c. CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
d.
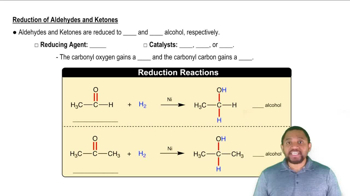
Why do aldehydes and ketones have lower boiling points than alcohols with similar molecular weights? Why are their boiling points higher than those of alkanes with similar molecular weights?
What ketones or aldehydes might be reduced to yield the following alcohols?
a.
b.
c. HOCH2–CH2–CH2OH
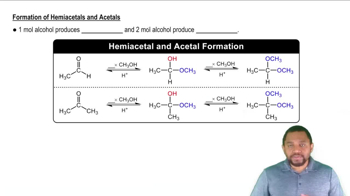
Draw the structures of the hemiacetals or hemiketals formed in these reactions:
b.
For each compound shown next, determine whether it is a hemiacetal, a hemiketal, an acetal, or a ketal.
a.
b.
c.
d.