A fundamental difference between aldehydes and ketones is that one can be oxidized to carboxylic acids but the other cannot. Which is which? Give an example of a test to differentiate aldehydes from ketones.

Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An aldehyde with four carbons
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Aldehyde Structure
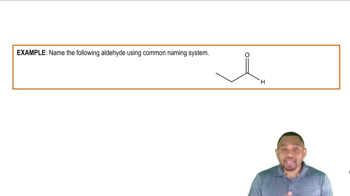
Carbon Chain Length

Structural Representation

Glucose is the major sugar in mammalian blood. We often see it represented as either the "free aldehyde" or the cyclic hemiacetal forms shown here. Of the two forms of glucose, the cyclic hemiacetal is the preferred form found in blood. Can you suggest two reasons why?
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
a. A 6-carbon cyclic ketone with a methyl group on the beta carbon
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
c. An alpha-bromoaldehyde, C4H7BrO
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
b. An 8-carbon ketone with six carbons as its longest chain
Draw a structure for a compound that meets each of the following descriptions:
d. A cyclic alpha-hydroxyketone, C5H8O2
