Draw the structures of the ammonium ions formed when the amines in Problem 16.30 are treated with acid.
a. N-Methylpentylamine
b. N-Ethylcyclobutylamine
c. p-Propylaniline

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


Draw the structures of the ammonium ions formed when the amines in Problem 16.30 are treated with acid.
a. N-Methylpentylamine
b. N-Ethylcyclobutylamine
c. p-Propylaniline
Complete the following equations (hint: remember that a nitrogen with three groups bound to it has a lone pair and one with four does not):
a.
Complete the following equations. (Hint: Remember that a nitrogen with three groups bound to it has a lone pair and one with four does not)
a.
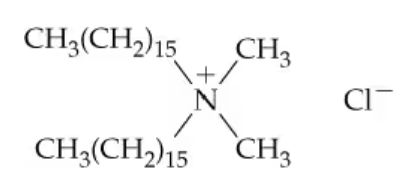
Choline has the following structure. Do you think that this substance reacts with aqueous hydrochloric acid? If so, what is the product? If not, why not?
Which is the stronger base, trimethylamine or ammonia? In which direction will the following reaction proceed?
How do amines differ from analogous alcohols in (a) odor, (b) basicity, and (c) boiling point?