Textbook Question
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
486
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


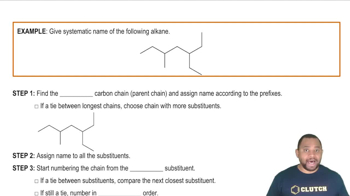
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. Ethyl 2-hydroxypropanoate
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
c.
Draw structures of the carboxylic acids and alcohols you would use to prepare each ester in Problem 17.54.
a.
b.
c. Cyclohexyl acetate
d. Phenyl-o-hydroxybenzoate
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
a. 3-Methylpentanamide
Give systematic names for the following structures and structures for the names:
b. N-Phenylacetamide