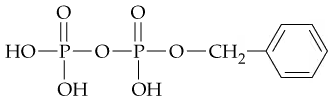
When both the carboxylic acid and the amine are in the same molecule, amide formation produces lactams. A lactam is a cyclic amide, where the amide group is part of the ring. Draw the structure of the product(s) obtained from acid hydrolysis of these lactams.
a.