Household soap is a mixture of the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids that arise from saponification of animal fat.
b. Draw the structures of the soap molecules produced in the following reaction:

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Household soap is a mixture of the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain carboxylic acids that arise from saponification of animal fat.
b. Draw the structures of the soap molecules produced in the following reaction:
A simple polyamide can be made from ethylenediamine and oxalic acid (Table 17.1). Draw the polymer formed when three units of ethylenediamine reacts with two units of oxalic acid.
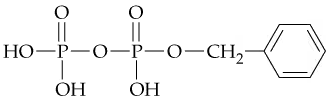
In the following compound
a. Identify the phosphate ester linkage.
Cyclic ribose nucleotide phosphates, such as cyclic AMP (cAMP), are important signaling agents in living cells; all have the general structure shown here. What kind of linkage holds the phosphate to the ribose (see arrows; ribose is highlighted in blue)?
What is the difference between a phosphate diester and an ester of a diphosphate? Give an example of each.
Propanamide and methyl acetate have about the same molar mass, both are quite soluble in water, and yet the boiling point of propanamide is 213 °C, whereas that of methyl acetate is 57 °C. Explain.