Use the three-letter abbreviations to name all tripeptides that contain valine, methionine, and leucine.

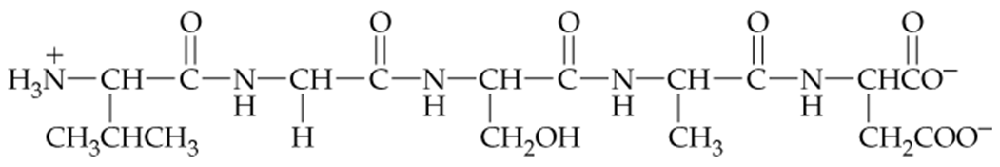
Identify the amino acids present in the peptide shown and name the peptide using the three-letter abbreviations.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Amino Acids

Peptide Structure
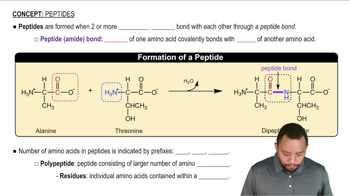
Three-Letter Abbreviations

Write structural formulas for the two dipeptides that contain leucine and aspartate.
The endorphins are a group of naturally occurring neurotransmitters that act in a manner similar to morphine to control pain. Research has shown that the biologically active parts of the endorphin molecules are simple pentapeptides called enkephalins. Draw the structure of the methionine enkephalin with the sequence Tyr-Gly-Gly-Phe-Met. Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids.
Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids of the peptide.
What is the sequence of atoms along the "backbone" of a protein?
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
a. Draw the complete structural formula of bradykinin.
