Textbook Question
Identify the amino acids present in the peptide shown and name the peptide using the three-letter abbreviations.
306
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
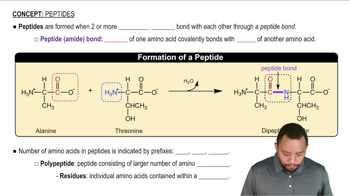


Identify the amino acids present in the peptide shown and name the peptide using the three-letter abbreviations.
Identify the N-terminal and C-terminal amino acids of the peptide.
What is the sequence of atoms along the "backbone" of a protein?
Bradykinin, a peptide that helps to regulate blood pressure, has the primary structure Arg-Pro-Pro-Gly-Phe-Ser-Pro-Phe-Arg.
b. Bradykinin has a very kinked secondary structure. Why?
Give an example of a protein containing primarily alpha-helices. Is this a fibrous or globular protein?
What kind of bond would you expect between the side chains of the following amino acids?
b. Alanine and leucine