Textbook Question
Cortisol levels rise under stressful conditions. Oxytocin can induce relaxation and romantic feelings. What type of protein are cortisol and oxytocin?
146
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

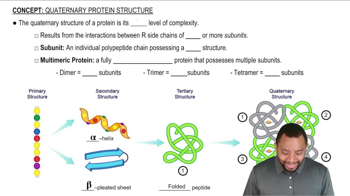

Cortisol levels rise under stressful conditions. Oxytocin can induce relaxation and romantic feelings. What type of protein are cortisol and oxytocin?
Consult Table 18.3 and draw alanine. Label the functional groups and give the three-letter abbreviation and the one-letter abbreviation. What group does the side chain fall into?
Examine the ball-and-stick model of valine below. Identify the carboxyl group, the amino group, and the R group.
<IMAGE>