Textbook Question
What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
a. Peptide bonds between amino acids?
1047
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


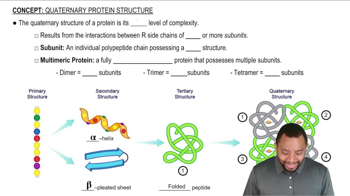
What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
a. Peptide bonds between amino acids?
What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
b. Hydrogen bonds between backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms attached to backbone nitrogen atoms?
How do the following noncovalent interactions help to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein? Give an example of a pair of amino acids that could give rise to each interaction.
a. Hydrophobic interactions
Give an example of a protein that has quaternary structure. How many polypeptide chains are present in this protein?
Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
a. Heat
Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
b. Strong acids