What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
b. Hydrogen bonds between backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms attached to backbone nitrogen atoms?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
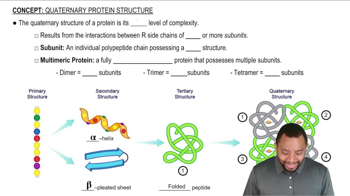

What level of protein structure is determined by the following:
b. Hydrogen bonds between backbone carbonyl oxygen atoms and hydrogen atoms attached to backbone nitrogen atoms?
How do the following noncovalent interactions help to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein? Give an example of a pair of amino acids that could give rise to each interaction.
a. Hydrophobic interactions
How do the following interactions help to stabilize the tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein? Give an example of a pair of amino acids that could give rise to each interaction.
b. Disulfide bonds
Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
a. Heat
Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
b. Strong acids
Explain how a protein is denatured by the following:
c. Organic solvents