Textbook Question
Is phenylalanine hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Explain why.
1656
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
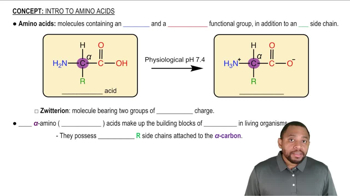


Is phenylalanine hydrophilic or hydrophobic? Explain why.
At neutral pH, which of the following amino acids has a net positive charge, which has a net negative charge, and which is neutral? (Hint: Draw the various charged forms of each amino acid before deciding.)
a. Asparagine
b. Lysine
c. Proline
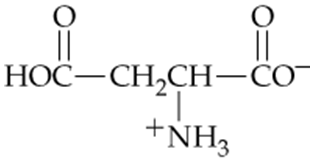
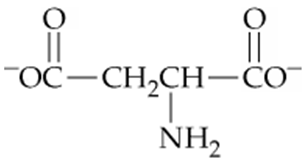
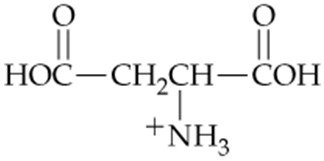
Which of the following forms of aspartic acid would you expect to predominate at low pH, neutral pH, and high pH?
a.
b.
c.
Proteins are usually least soluble in water at their isoelectric points. Explain.
How could you make the zwitterion of aspartic acid more soluble in water?
Use the three-letter abbreviations to name all tripeptides that contain valine, methionine, and leucine.