How would you classify the link between the monosaccharides in cellobiose?

Consider the trisaccharide A, B, C shown in Problem 20.23.
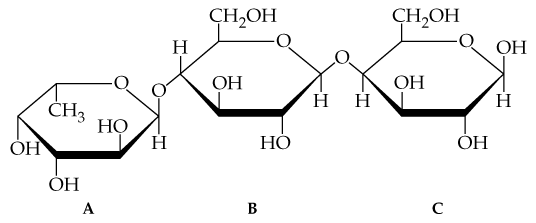
a. Identify the hemiacetal and acetal linkages.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
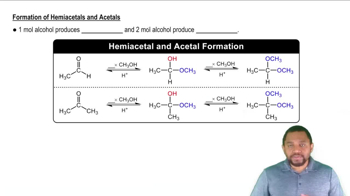
Hemiacetal Linkage
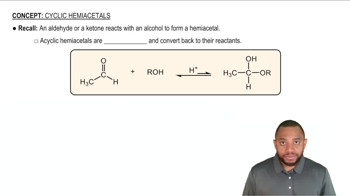
Acetal Linkage
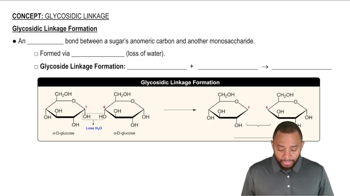
Glycosidic Bond
During the digestion of starch from potatoes, the enzyme α-amylase catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch into maltose. Subsequently, the enzyme maltase catalyzes the hydrolysis of maltose into two glucose units. Write an equation (in words) for the enzymatic conversion of starch to glucose. Classify each of the carbohydrates in the equation as a disaccharide, monosaccharide, or polysaccharide.
Identify the following as diastereomers, enantiomers, and/or anomers.
(a) β-D-fructose and β-D-fructose
(b) D-galactose and L-galactose
(c) L-allose and D-glucose (both aldohexoses)
Consider the trisaccharide A, B, C shown in Problem 20.23.
c. State the numbers of the carbon atoms that form glycosidic linkages between monosaccharide A and monosaccharide B.
Hydrolysis of both glycosidic bonds in the following trisaccharide A, B, C yields three monosaccharides.
c. Draw the Fischer projections for the three monosaccharides.
Are one or more of the disaccharides maltose, lactose, cellobiose, and sucrose part of the trisaccharide in Problem 20.23? If so, identify which disaccharide and its location. (Hint: Look for an α-1,4 link, β-1,4 link, or 1,2 link, and then determine if the correct monosaccharides are present.)
