Textbook Question
What key metabolic intermediate is formed from the catabolism of all three major classes of foods: carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins?
907
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
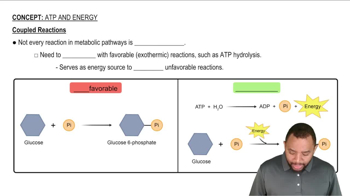

What key metabolic intermediate is formed from the catabolism of all three major classes of foods: carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins?
Why is ATP sometimes called a high-energy molecule?
What general kind of chemical reaction does ATP participate in?
Write the reaction for the hydrolysis of 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP using the curved-arrow symbolism.
FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
a. When a molecule is dehydrogenated, is FAD oxidized or reduced?
FAD is a coenzyme for dehydrogenation.
b. Is FAD an oxidizing agent or a reducing agent?