Textbook Question
How many moles of ATP are generated from the catabolism of fructose (by glycolysis) in
(a) liver cells?
717
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


How many moles of ATP are generated from the catabolism of fructose (by glycolysis) in
(a) liver cells?
How many moles of ATP are generated from the catabolism of fructose (by glycolysis) in
(b) muscle cells?
Which of the following conversions would you expect to consume energy and which would you expect to yield energy based on the final oxidation state of the coenzymes involved in each reaction?
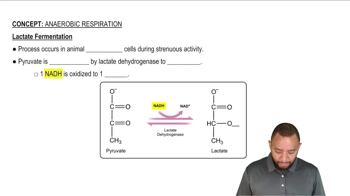
a. pyruvate → lactate
Why is it important for the cell that the NADH produced when pyruvate is converted to lactate be converted back to NAD+?
What are the characteristics of Type I diabetes?
What are the characteristics of Type II diabetes?