Show the structure of a cerebroside made up of D-galactose, sphingosine, and myristic acid.
Ch.23 Lipids

Chapter 23, Problem 72
Which process requires energy—passive or active transport? Why is energy sometimes required to move solute across the cell membrane?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the difference between passive and active transport: Passive transport does not require energy because it relies on the natural movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration (down the concentration gradient). Active transport, on the other hand, requires energy because it moves molecules against their concentration gradient (from low to high concentration).
Recognize why energy is required in active transport: Moving solutes against their concentration gradient is not a spontaneous process. It requires an input of energy, typically in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), to drive the transport proteins that facilitate this movement.
Consider the role of the cell membrane: The cell membrane is selectively permeable, meaning it regulates what enters and exits the cell. For certain solutes that cannot pass freely through the membrane or are being moved against their gradient, energy is needed to assist their transport.
Identify examples of active transport: Processes like the sodium-potassium pump (Na⁺/K⁺ pump) are classic examples of active transport. This pump uses ATP to move sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, maintaining essential concentration gradients.
Summarize the importance of energy in active transport: Energy is required to maintain concentration gradients, import essential nutrients, and remove waste products, all of which are critical for the cell's survival and proper functioning.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
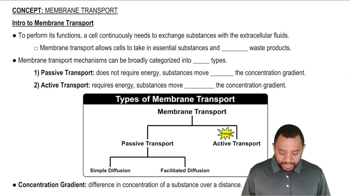
Active Transport
Active transport is a cellular process that requires energy to move molecules against their concentration gradient, from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. This energy is typically derived from ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and is essential for maintaining cellular homeostasis and nutrient uptake.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Membrane Transport Concept 1
Passive Transport
Passive transport is the movement of substances across a cell membrane without the use of energy. This process occurs along the concentration gradient, meaning substances move from areas of higher concentration to areas of lower concentration. Examples include diffusion and osmosis, which allow cells to maintain equilibrium without expending energy.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Membrane Transport Concept 1
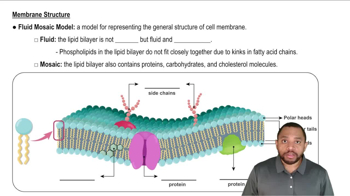
Cell Membrane Dynamics
The cell membrane is a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the entry and exit of substances. Understanding its dynamics is crucial for grasping why certain processes require energy; for instance, when ions or larger molecules need to be transported against their natural flow, energy is necessary to facilitate this movement and maintain the cell's internal environment.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Cell Membranes Concept 2
Related Practice
Textbook Question
800
views
Textbook Question
Draw the structure of a glycerophospholipid that contains palmitic acid, oleic acid, and the phosphate bonded to propanolamine.
882
views
Textbook Question
Cardiolipin, a compound found in heart muscle, has the following structure. What products are formed if all ester bonds in the molecule are saponified by treatment with aqueous NaOH?
735
views
Textbook Question
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
a. NO (nitrous oxide)
710
views
Textbook Question
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
c. Ca2+
1007
views
Textbook Question
Based on the information in Section 23.7, how would you expect each of these common metabolites to cross the cell membrane?
a. CO
905
views
