Starting with acetyl-S-enzyme-1 and malonyl-CoA, how many molecules of acetyl-CoA are needed to synthesize an 18-carbon fatty acid (C18:0)? How many molecules of CO2 are released in this process?
Ch.24 Lipid Metabolism

Chapter 24, Problem 12d
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
d. Which lipoprotein contains “bad cholesterol” from a vascular disease risk standpoint?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
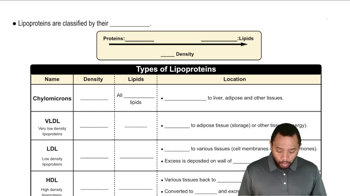
Understand the role of lipoproteins: Lipoproteins are complexes of lipids and proteins that transport lipids (fats) through the bloodstream. The four main types are chylomicrons, HDL (high-density lipoprotein), LDL (low-density lipoprotein), and VLDL (very-low-density lipoprotein). Each has a specific function and composition.
Recall the function of LDL: LDL is responsible for transporting cholesterol from the liver to cells throughout the body. However, excess LDL cholesterol can deposit in the walls of arteries, leading to plaque formation and increasing the risk of vascular diseases such as atherosclerosis.
Understand why LDL is considered 'bad cholesterol': From a vascular disease risk standpoint, LDL is termed 'bad cholesterol' because its accumulation in arterial walls can lead to blockages, reducing blood flow and potentially causing heart attacks or strokes.
Differentiate LDL from other lipoproteins: HDL is known as 'good cholesterol' because it helps remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and transports it back to the liver for excretion. VLDL primarily carries triglycerides, and chylomicrons transport dietary lipids from the intestines to other tissues.
Conclude that the lipoprotein containing 'bad cholesterol' is LDL, based on its role in cholesterol transport and its association with increased vascular disease risk.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
2mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Lipoproteins
Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of lipids and proteins that transport fats through the bloodstream. They vary in density and composition, influencing their function and role in health. The main types include chylomicrons, very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL), low-density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL), each serving distinct purposes in lipid metabolism.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein)
LDL, often referred to as 'bad cholesterol,' is a type of lipoprotein that carries cholesterol from the liver to the cells. High levels of LDL can lead to the buildup of cholesterol in the arteries, increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis. Monitoring LDL levels is crucial for assessing vascular disease risk.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Lipoproteins for Transport Concept 2
Cholesterol and Cardiovascular Risk
Cholesterol is a waxy substance found in the blood, essential for building cells but harmful in excess. The balance between different types of cholesterol, particularly the ratio of LDL to HDL (high-density lipoprotein), is critical for cardiovascular health. Elevated LDL levels are associated with a higher risk of vascular diseases, making it important to manage cholesterol levels through diet and lifestyle.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Steroids Example 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
983
views
Textbook Question
Oxygen is not a reactant in the β oxidation of fatty acids. Can β oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
608
views
Textbook Question
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
a. Which lipoprotein has the lowest density? Why?
1391
views
Textbook Question
One strategy used in many different biochemical pathways is an initial investment of energy early on and a large payoff in energy at the end of the pathway. How is this strategy utilized in the catabolism of fats?
586
views
Textbook Question
Compare the differences between β oxidation and fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis). Are these pathways the reverse of each other?
692
views
Textbook Question
Why do lipids make you feel full for a long time after a meal?
632
views
