Textbook Question
Oxygen is not a reactant in the β oxidation of fatty acids. Can β oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
608
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
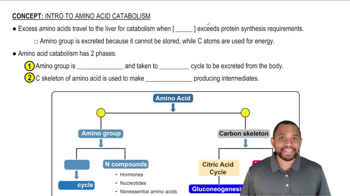

Oxygen is not a reactant in the β oxidation of fatty acids. Can β oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
a. Which lipoprotein has the lowest density? Why?
Identify each lipoprotein described here as either chylomicron, HDL, LDL, or VLDL.
d. Which lipoprotein contains “bad cholesterol” from a vascular disease risk standpoint?
Compare the differences between β oxidation and fatty acid synthesis (lipogenesis). Are these pathways the reverse of each other?
Why do lipids make you feel full for a long time after a meal?
What is the purpose of bile acids in lipid digestion?