How are long-chain fatty acids released from triacylglycerides transported through the bloodstream?

Which of the following classifications apply to the formation of 3-hydroxybutyrate from acetoacetate?
a. Condensation
b. Hydrolysis
c. Oxidation
d. Reduction
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
3-Hydroxybutyrate and Acetoacetate
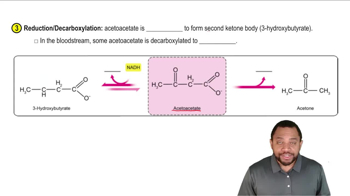
Reduction Reaction
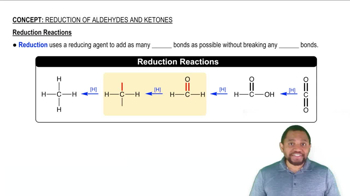
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions

How many molecules of acetyl-CoA are produced by catabolism of the following fatty acids, and how many β oxidations are needed?
a. Palmitic acid, CH3(CH2)14COOH
Look back at the reactions of the citric acid cycle (Figure 21.8) and identify the three reactions in that cycle that are similar to the first three reactions of the β oxidation of a fatty acid.
<IMAGE>
Consider the reactions of ketogenesis.
c. What is the essential role of ketone bodies during prolonged starvation?
Starting with acetyl-S-enzyme-1 and malonyl-CoA, how many molecules of acetyl-CoA are needed to synthesize an 18-carbon fatty acid (C18:0)? How many molecules of CO2 are released in this process?
Oxygen is not a reactant in the β oxidation of fatty acids. Can β oxidation occur under anaerobic conditions? Explain.
