What is the structure of the α-keto acid formed by transamination of the amino acid phenylalanine (Phe)?

Three metabolites that can result from the breakdown of the carbon skeleton of amino acids are ketone bodies, acetyl-CoA, and glucose. Briefly describe how each of these metabolites can be produced from amino acid catabolism.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Amino Acid Catabolism
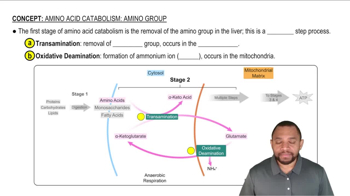
Acetyl-CoA Production

Ketone Bodies

Unlike most amino acids, branched-chain amino acids are broken down in tissues other than the liver. Using Table 18.3, identify the three amino acids with branched-chain R groups. For any one of these amino acids, write the equation for its transamination.
<IMAGE>
Fumarate from step 3 of the urea cycle may be recycled into aspartate for use in step 2 of the cycle. The sequence of reactions for this process is
a.
b.
c.
Classify each reaction as one of the following:
1. Oxidation
2. Reduction
3. Transamination
4. Elimination
5. Addition
Define what an “essential” nutrient is and explain how it differs from a “nonessential” nutrient.
In the liver, the relative activity of ornithine transcarbamylase is high, that of argininosuccinate synthetase is low, and that of arginase is high. Why is it important that ornithine transcarbamylase activity be high in the liver? What might be the consequence if arginase activity is low or defective?
What citric acid cycle intermediates are precursors to amino acids?
