Identify the amino acid for which the codon GAG codes, and what other codon could encode for this same amino acid?
Ch.26 Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis

Chapter 26, Problem 23
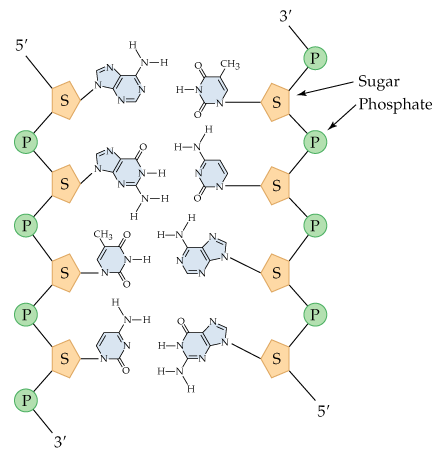
Copy the diagram and use dotted lines to indicate where hydrogen bonding occurs between the complementary strands of DNA. What is the sequence of each strand of DNA drawn (remember that the sequence is written from the 5′ to 3′ end)?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the complementary base pairs in DNA: Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) via two hydrogen bonds, and Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G) via three hydrogen bonds.
Examine the provided DNA diagram and locate the nitrogenous bases on each strand. Ensure you understand the orientation of the strands (5′ to 3′ direction).
Draw dotted lines between the complementary bases to represent hydrogen bonds: two dotted lines between A and T, and three dotted lines between C and G.
Determine the sequence of the complementary strand by reading the bases on the opposite strand in the 5′ to 3′ direction. Remember that the strands are antiparallel, so the complementary strand runs in the opposite direction (3′ to 5′).
Write the sequence of each strand explicitly, ensuring the correct 5′ to 3′ orientation for both strands. Double-check that the base pairing and orientation are consistent with the rules of DNA structure.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
8mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Hydrogen Bonding in DNA
Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak chemical bond that occurs between the nitrogenous bases of DNA strands. In DNA, adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T) through two hydrogen bonds, while cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G) through three hydrogen bonds. This specific pairing is crucial for the stability of the DNA double helix structure and ensures accurate replication and transcription.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Hydrogenation Reactions Concept 1
DNA Strand Orientation
DNA strands have a directionality defined by their sugar-phosphate backbone, which has a 5' (five-prime) end and a 3' (three-prime) end. The 5' end has a phosphate group, while the 3' end has a hydroxyl group. When writing the sequence of a DNA strand, it is essential to start from the 5' end and proceed to the 3' end, as this orientation is critical for understanding replication and transcription processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Intro to DNA Replication Concept 1
Complementary Base Pairing
Complementary base pairing refers to the specific pairing of nitrogenous bases in DNA, where A pairs with T and C pairs with G. This concept is fundamental to the structure of DNA, as it allows for the formation of the double helix and ensures that genetic information is accurately copied during cell division. Understanding this pairing is essential for drawing the correct sequences and indicating hydrogen bonds in a DNA diagram.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Base Pairing Concept 1
Related Practice
Textbook Question
838
views
Textbook Question
What amino acids do the following sequences code for?
a. AUC
753
views
Textbook Question
What amino acid sequence is coded for by the mRNA base sequence CUC-AUU-CCA-UGC-GAC-GUA?
1034
views
Textbook Question
Copy the following simplified drawing of a DNA replication fork:
a. On the drawing, indicate the direction of synthesis of the new strand labeled A and the location of DNA polymerase on the strand.
594
views
Textbook Question
Gln-His-Pro-Gly is the sequence of a molecule known as progenitor thyrotropin-releasing hormone (pro-TRH). If we were searching for pro-TRH genes, we would need to know what sequence of bases in DNA we should be looking for. Use the following boxes to indicate answers to parts (a)–(d).
a. What RNA sequence could code for these four amino acids?
906
views
Textbook Question
What is the difference between a gene and a chromosome?
1120
views
