Textbook Question
What amino acid sequence is coded for by the mRNA base sequence CUC-AUU-CCA-UGC-GAC-GUA?
1034
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance


What amino acid sequence is coded for by the mRNA base sequence CUC-AUU-CCA-UGC-GAC-GUA?
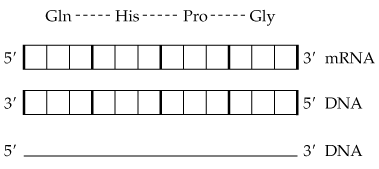
Copy the diagram and use dotted lines to indicate where hydrogen bonding occurs between the complementary strands of DNA. What is the sequence of each strand of DNA drawn (remember that the sequence is written from the 5′ to 3′ end)?
Copy the following simplified drawing of a DNA replication fork:
a. On the drawing, indicate the direction of synthesis of the new strand labeled A and the location of DNA polymerase on the strand.
What is the difference between a gene and a chromosome?
What are the two major components of chromatin?
What genetic information does a single gene contain?